Circuit breakers are vital for keeping your home’s electrical system safe and functional. This guide gives you expert tips and crucial info to help you choose wisely.
Whether you’re a homeowner or a DIY enthusiast, this guide has you covered. We’ll walk you through everything, from understanding different breaker types and ratings to the essential factors to consider during selection. You’ll be well-equipped to pick the right circuit breaker for your needs.
Let’s jump in and navigate the world of circuit breakers together, so your home’s electrical system remains safe and efficient!
What Is A Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is a critical component of your home’s electrical system that safeguards against electrical overloads and short circuits. It acts as a safety device, automatically interrupting the flow of electricity when it detects an abnormal condition in the circuit.
A circuit breaker is like a switch that can be manually or automatically turned off to prevent electrical damage or fire hazards. When an electrical overload or short circuit occurs, the circuit breaker trips and interrupts the flow of electricity, protecting the wiring and connected appliances from potential damage.
The primary purpose of a circuit breaker is to ensure the safety of your home’s electrical system and the devices connected to it. By quickly detecting and interrupting faulty electrical conditions, circuit breakers minimise the risk of electrical fires and protect property and human lives.
![2023 07 Label On Circuit Breaker Label Circuit Breaker]()
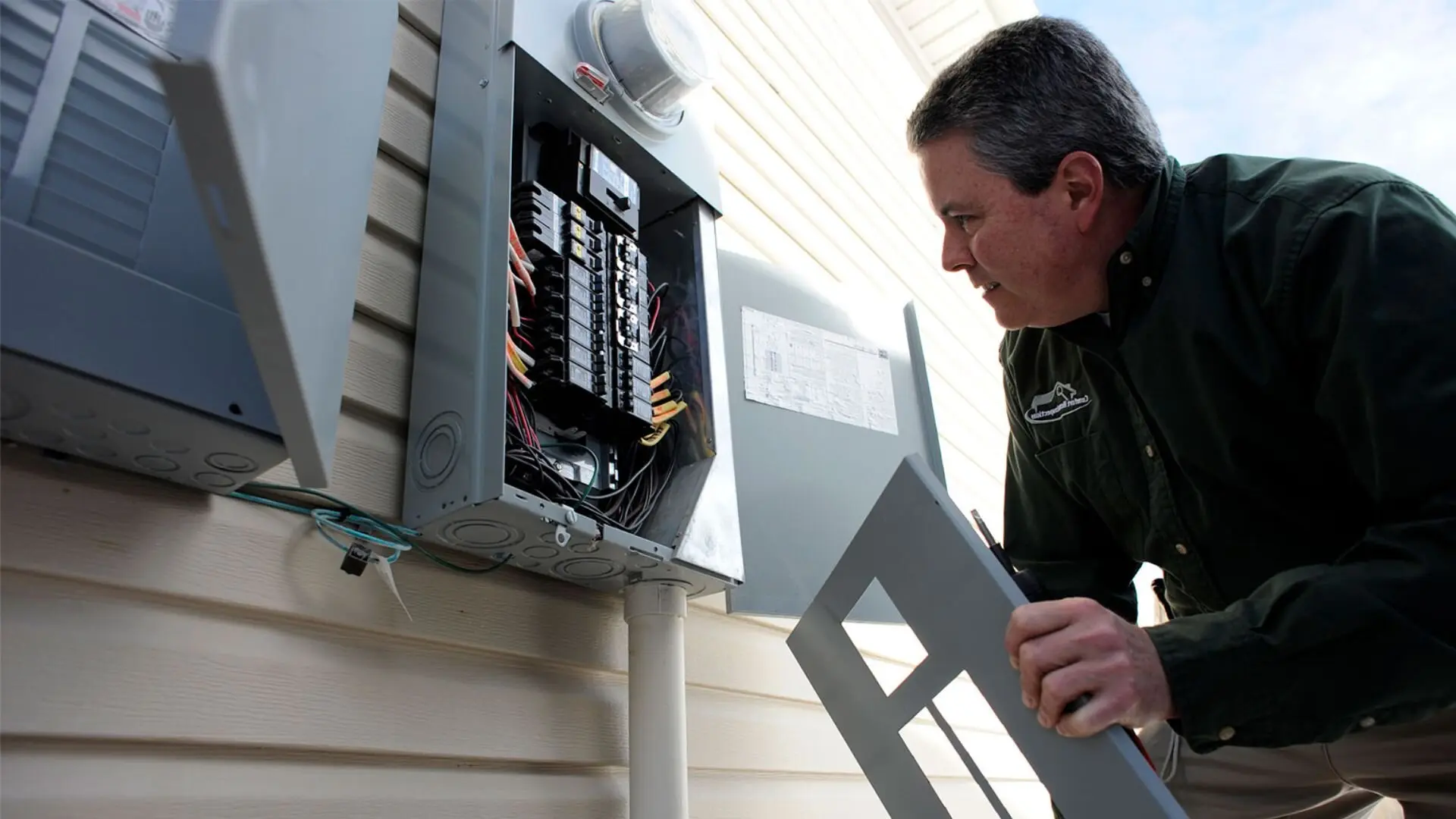
Typically, you’ll find circuit breakers in a distribution board’s electrical panel or switchboard. It’s essentially the heart of your home’s electrical system. Each circuit—whether for lighting, outlets, or specific appliances—gets its dedicated breaker here.
When a circuit breaker trips, it moves to an “off” position, breaking the electrical connection and stopping the flow of electricity. To restore power, manually reset the tripped breaker by moving it back to the “on” position. However, addressing the cause of the circuit overload or short circuit is crucial before resetting the breaker.
Types Of Circuit Breakers
Choosing the right circuit breaker for your home means getting familiar with the various types and what each one does. Let’s explore the common breakers you’ll encounter in residential settings:
Standard Circuit Breakers
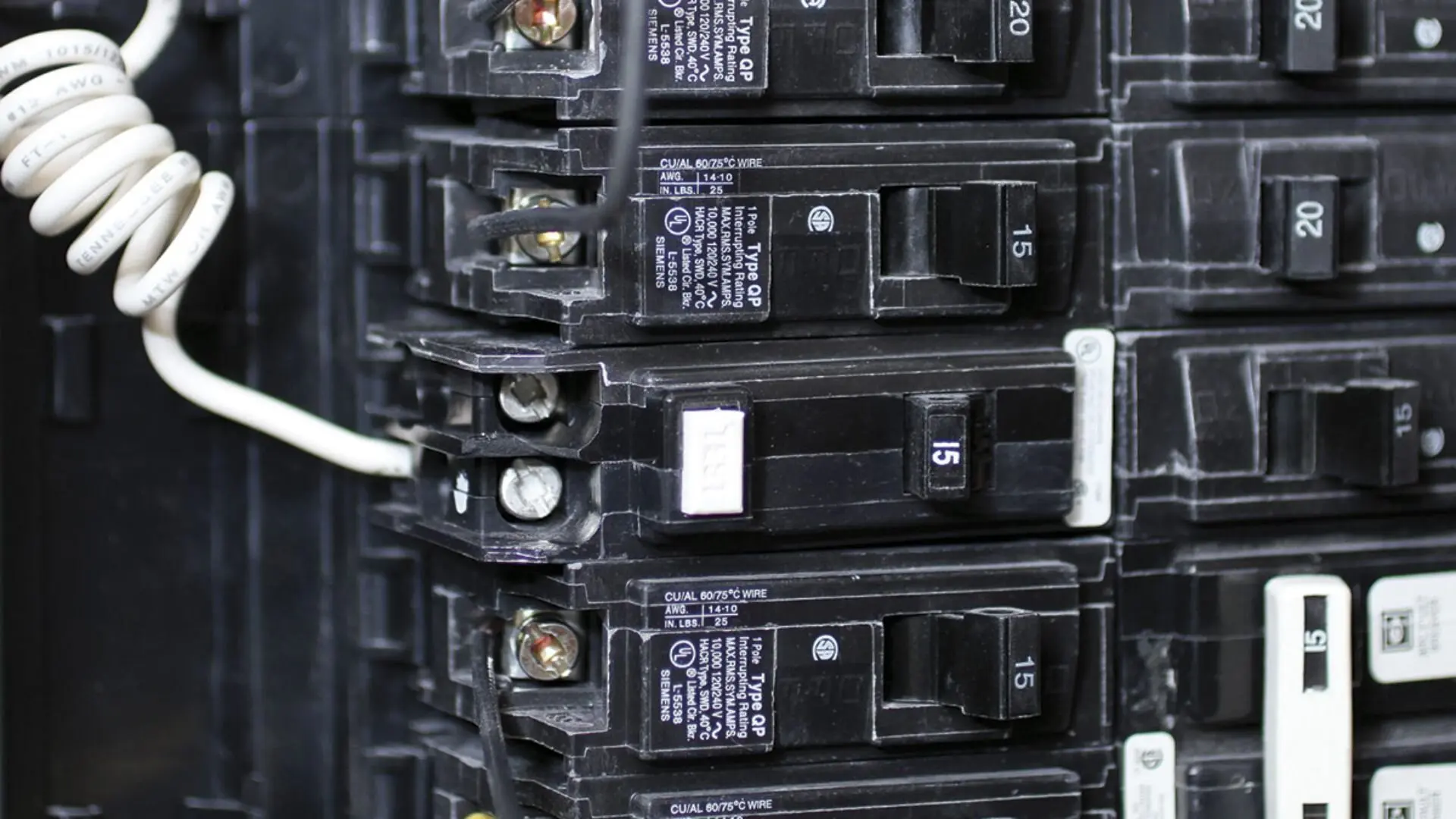
The most commonly used type is also known as single-pole circuit breakers. They protect individual circuits and are designed to handle a specific current rating. Standard breakers are suitable for general lighting and outlet circuits in residential homes.
AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) Breakers
AFCI breakers are designed to detect and mitigate the risk of electrical arcing, which can cause fires. They provide extra protection by monitoring the circuit for any abnormal arcing conditions. AFCI breakers are commonly required in bedrooms, living rooms, and other areas where electrical fires may occur due to damaged or aged wiring.
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) Breakers
GFCI breakers are designed to protect against ground faults, which happen when electrical currents escape the intended circuit path and flow through a person or an unintended surface. These breakers are commonly used in areas with a higher risk of electrical shocks, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets.
![2023 07 Afci Vs Gfci Afci Gfci]()
Combination Arc Fault/Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (CAFCI/GFCI) Breakers
These breakers combine the features of AFCI and GFCI breakers, offering protection against both arc faults and ground faults. They are commonly used in areas where both types of protection are required, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms.
It’s important to note that circuit breaker types may vary depending on your specific electrical system and local electrical codes. Consulting with a qualified electrician or electrical professional is highly recommended to determine the appropriate breakers for your home.
Understanding Circuit Breaker Ratings
Getting the circuit breaker ratings right is key to ensuring they’ll work well with your home’s electrical system. It’s worthwhile to have a solid grasp of these ratings for wise selection and safe operation. Let’s dive into what makes these ratings so important:
![2023 07 Electrician Looking At Switchboard And Circuit Breakers Electrician Switchboard Circuit Breakers]()
Current Rating
The current rating of a circuit breaker indicates the maximum current it can safely handle without tripping. It is measured in amperes (A). When choosing a breaker, ensure that its current rating matches or exceeds the anticipated current load of the circuit it will protect. It’s essential to avoid overloading a circuit by using a breaker with a lower current rating than required.
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of a circuit breaker specifies the maximum voltage it can safely handle. It is crucial to select a circuit breaker with a rating that matches the voltage of your home’s electrical system. A breaker with an insufficient voltage rating can lead to electrical hazards and compromised protection.
Interrupting Rating
The interrupting rating, also known as the short-circuit current rating (SCCR), indicates the maximum short-circuit current level a breaker can safely interrupt. Short circuits can occur when an abnormal connection or fault in the electrical system causes a sudden surge of current. A breaker with a sufficient interrupting rating can safely interrupt the fault current and protect the electrical system from damage.
Trip Curve
Circuit breakers have different trip curves, which determine the breaker’s response time to an overcurrent condition. The trip curve indicates the relationship between the current magnitude and the time it takes for the circuit breaker to trip. Different trip curves are designed for specific applications, such as motor circuits, lighting circuits, or power distribution. Understanding the trip curve helps ensure the circuit breaker adequately responds to overcurrent situations without causing unnecessary tripping or compromising safety.
Factors To Consider When Selecting A Circuit Breaker
Selecting the right circuit breaker means looking at several factors to make sure it works well, keeps things safe, and fits with your electrical system. By weighing these elements, you’ll be positioned to make a decision that’s right for you. Here’s what you should keep an eye on when choosing a breaker:
![2023 07 Close Up Of Circuit Breakers Close Circuit Breakers]()
Electrical Load Analysis
Conduct an electrical load analysis to determine your home’s total power consumption and expected current demands. This analysis helps you understand each circuit’s capacity and load requirements, enabling you to choose circuit breakers with appropriate current ratings.
Compatibility With Existing Wiring
Evaluate the circuit breaker’s compatibility with your existing wiring infrastructure. Ensure the breaker’s size and connection type align with your electrical panel’s wiring. It’s essential to select breakers that fit correctly and provide reliable connections.
Type of Circuit Breaker
Consider your circuits’ specific requirements when selecting the breaker type. Common types include standard breakers, arc-fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs), ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), and combination breakers. Each type serves a specific purpose, such as protecting against overloads, short circuits, or ground faults. Choose the appropriate type based on the circuit’s intended function and safety requirements.
Brand Reputation and Quality
Opt for circuit breakers from reputable brands known for their quality and reliability. Well-established brands often adhere to industry standards and undergo rigorous testing to ensure their products meet safety regulations. Research customer reviews and ratings to gauge breaker brands’ overall satisfaction and performance.
Budget Considerations
Consider your budget when selecting breakers. While it’s essential to prioritise safety and quality, you can still find options that meet your requirements without exceeding your budget. Compare prices and features to find a balance between affordability and performance.
Future Expansion Plans
If you plan to expand your home in the future, such as adding new circuits or appliances, consider the flexibility and scalability of the breakers you choose. Opt for breakers that allow for easy additions and modifications to accommodate future electrical needs.
Professional Guidance
When in doubt or faced with complex electrical requirements, seek professional guidance from a qualified electrician or electrical contractor. They can assess your needs, recommend suitable breakers, and ensure proper installation for optimal performance and safety.
Safeguard Your Home With Circuit Breakers
Choosing the right circuit breaker for your home is a crucial decision that directly impacts the safety and functionality of your electrical system. By understanding the purpose, types, ratings, and factors to consider when selecting a circuit breaker, you can make an informed decision that ensures the optimal performance of your electrical system.
At Bright Force Electrical, we understand the importance of providing reliable electrical solutions tailored to our client’s needs. With our expertise and industry knowledge, we are dedicated to helping Sydney homeowners make well-informed choices regarding circuit breakers.
If you have any further questions or require assistance in selecting the right circuit breaker for your home, we are here to help. Contact Bright Force Electrical today to request a quote or schedule a phone call with one of our experienced electricians. With our professional and friendly service, you can trust us to deliver exceptional electrical solutions that prioritise safety and meet your unique requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the average lifespan of a circuit breaker?
Circuit breakers have an average lifespan of 30 to 40 years. However, this can vary depending on usage, environmental conditions, and manufacturer specifications. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections by a licensed electrician can help identify signs of wear or malfunction.
2. How can I determine the correct current rating for a circuit breaker?
To determine the appropriate current rating for a circuit breaker, you need to assess the electrical load of the circuit. Calculate the total power consumption of the connected appliances and devices and ensure the circuit breaker’s current rating exceeds this value. It’s advisable to consult an electrician for accurate load calculations and professional guidance.
3. What is the difference between AFCI and GFCI breakers?
AFCI (Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter) and GFCI (Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers serve different safety purposes. AFCI breakers detect dangerous arcing faults, which can cause electrical fires. GFCI breakers, on the other hand, protect against ground faults by detecting imbalances in electrical currents and preventing electric shock hazards. The specific application and electrical code requirements determine whether AFCI or GFCI breakers are necessary.
4. Can I use a circuit breaker with a higher current rating than required?
It is not recommended to use a circuit breaker with a higher current rating than necessary. Circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits and devices from excessive current flow. If you use a breaker with a higher rating, it may not trip as intended during overloads or short circuits, compromising the safety of your electrical system. Always use breakers with appropriate current ratings.
5. What are combination circuit breakers?
Combination breakers are a type of breaker that combines the functionalities of AFCI and GFCI protection in a single device. They provide enhanced safety by detecting both arc faults and ground faults. Combination breakers are often required in specific areas of the home, such as bedrooms and kitchens, where both types of protection are essential.
6. Can I replace a circuit breaker myself?
While some electrical tasks can be performed by homeowners, replacing a circuit breaker is best left to a qualified electrician. Circuit breaker replacement requires proper knowledge of electrical systems, adherence to safety protocols, and compliance with local building codes. Hiring a professional ensures the task is completed safely and accurately.