A circuit breaker acts like an automatic switch, stepping in to avert dangers such as short circuits and overloads. Unlike the old-school fuses, these clever devices can be reused and restore power automatically once they’ve tripped.
This guide dives into the ins and outs of circuit breakers, their purpose, how they work, and the different types you can choose from. By getting a grip on the basics, you’ll be equipped to make savvy decisions about the safety and upkeep of your electrical system. We’ve also tackled your pressing questions right here in this blog.
Read on to explore the world of circuit breakers and their invaluable role in ensuring the smooth operation of your electrical systems.
How Does a Circuit Breaker Work?
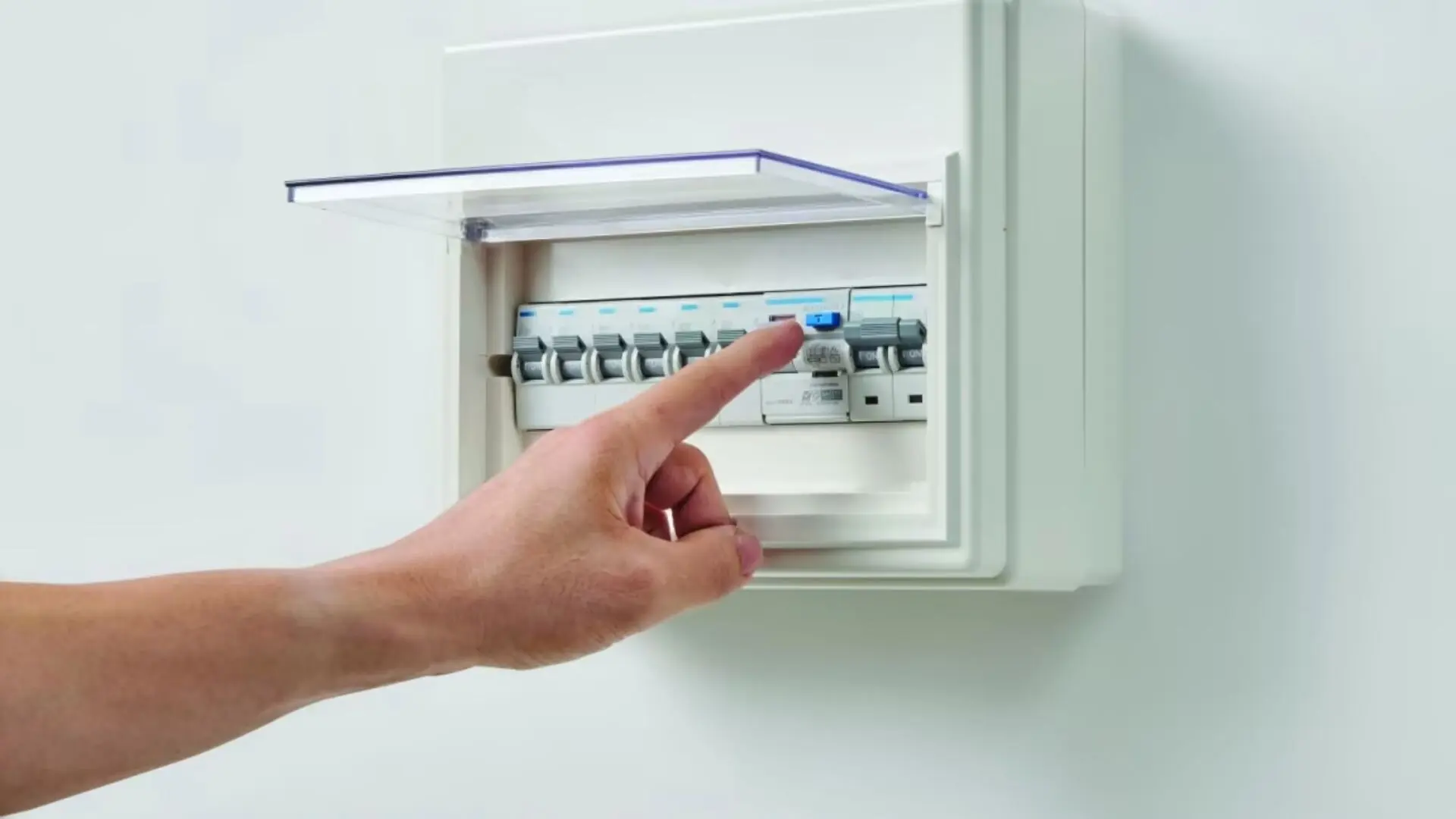
In any electrical setup, a circuit breaker is a vital part of the breaker or circuit panel. Its main job is to shield your circuits from overloads, short circuits, or other faults that could cause havoc or pose risks. Basically, it consists of a switch and a tripping mechanism. It cuts off the electric circuit automatically when things go awry to safeguard the circuit.
![2023 07 Flicking Circuit Breaker On Wall Flicking Circuit Breaker Wall]()
When an electrical circuit experiences an abnormal surge in current, such as during an overload or short circuit, the circuit breaker quickly detects the deviation. It responds by tripping - interrupting the flow of electrical current to the circuit. This immediate action will prevent overheating and potential damage to the electrical wiring, power source or connected devices.
Circuit breakers also play a vital role in protecting against ground faults, which occur when an electrical current deviates from its intended path and flows through unintended conductive materials. Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are specialised circuit breakers designed to detect ground faults and promptly shut off power to prevent an electrical shock and potential electrocution.
Multiple circuit breakers are arranged within a circuit breaker panel to control and protect various electrical circuits throughout a building or property. Each circuit breaker is assigned to a specific electrical circuit and has a defined current rating, indicating the maximum amount of electrical current it can safely handle.
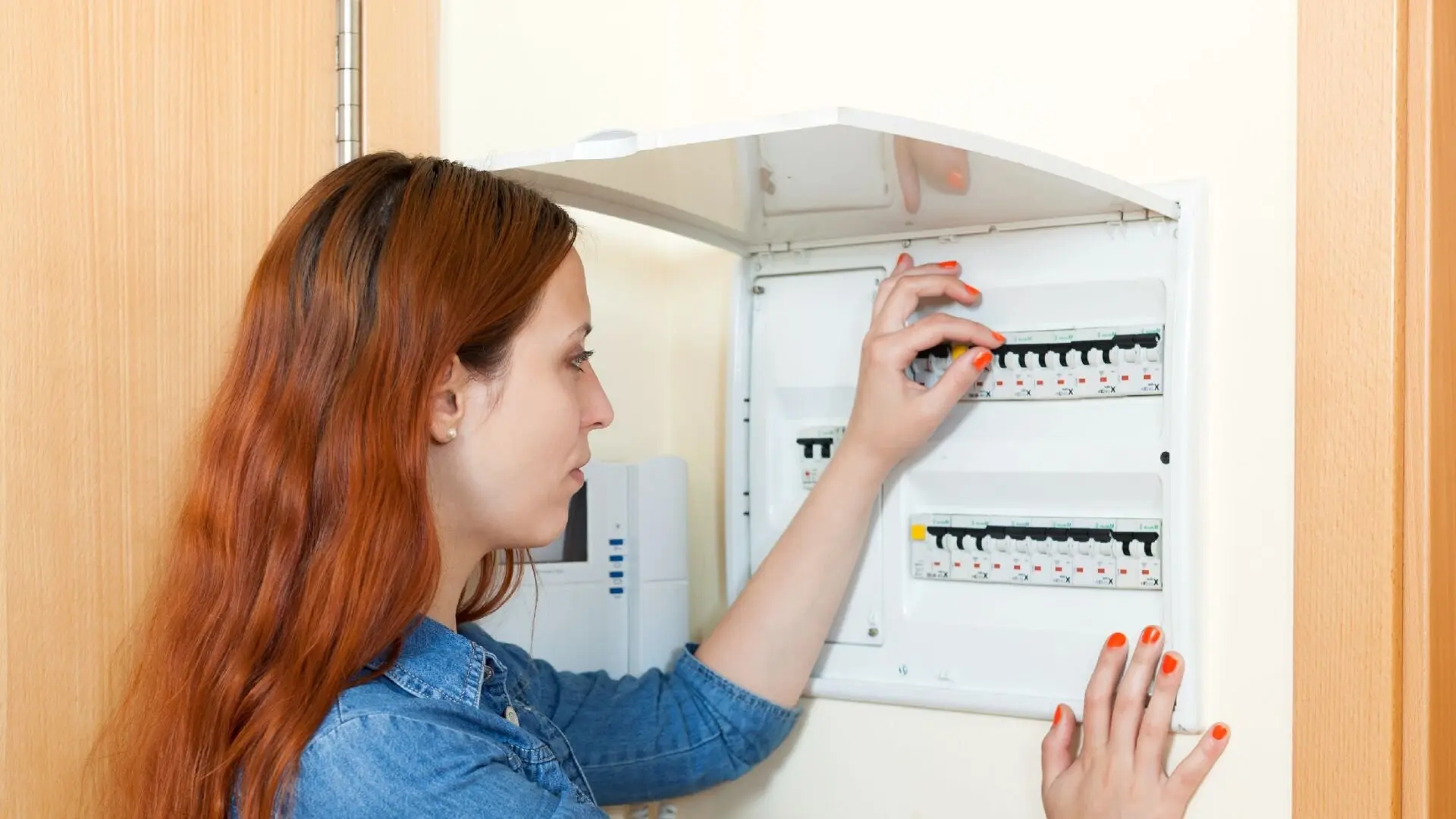
Why Are Circuit Breakers Important?
![2023 07 Woman Switching On Circuit Breaker Woman Switching Circuit Breaker]()
One of the primary reasons for the importance of circuit breakers is their role in providing short-circuit protection. A short circuit occurs when a hot wire comes into direct contact with a neutral wire or another hot wire and triggers a large amount of current flowing through the circuit. Without proper protection, this can result in overheating, electrical fires, and damage to electrical appliances and wiring.
Circuit breakers, installed within the breaker panel or circuit breaker box, play a crucial role in safeguarding against short circuits. When a short circuit occurs, the circuit breaker detects excessive current and interrupts the flow.
This action prevents damage to electrical appliances, wiring, and other connected devices, ensuring the electrical system’s safety. Circuit breakers, especially double-pole breakers, protect against electrical shocks when someone comes into contact with a live wire or faulty electrical equipment. Circuit breakers prevent life-threatening electrical shocks by quickly interrupting the circuit upon detecting abnormal current flow.
Circuit breakers are pretty handy at managing the power needs of different devices hooked up to the same circuit. They skillfully juggle the flow of electricity to multiple outlets, making sure your wiring and gadgets get the juice they need without risking an overload.
They’re built with insulating materials to keep their insides safe and sound, ensuring they work like a charm. Besides protecting your wires, circuit breakers have plenty of perks over old-school fuse boxes. Fuses need replacing every time they blow, but circuit breakers are a breeze to reset after they trip. This makes your life easier by cutting down on replacement and maintenance time.
Overall, the importance of circuit breakers cannot be overstated. From providing short circuit protection and preventing electrical shocks to offering convenience and flexibility, circuit breakers are indispensable components of our electrical systems. Their ability to detect and respond to abnormalities in electrical currents helps maintain the safety, integrity, and efficient operation of our homes and businesses.
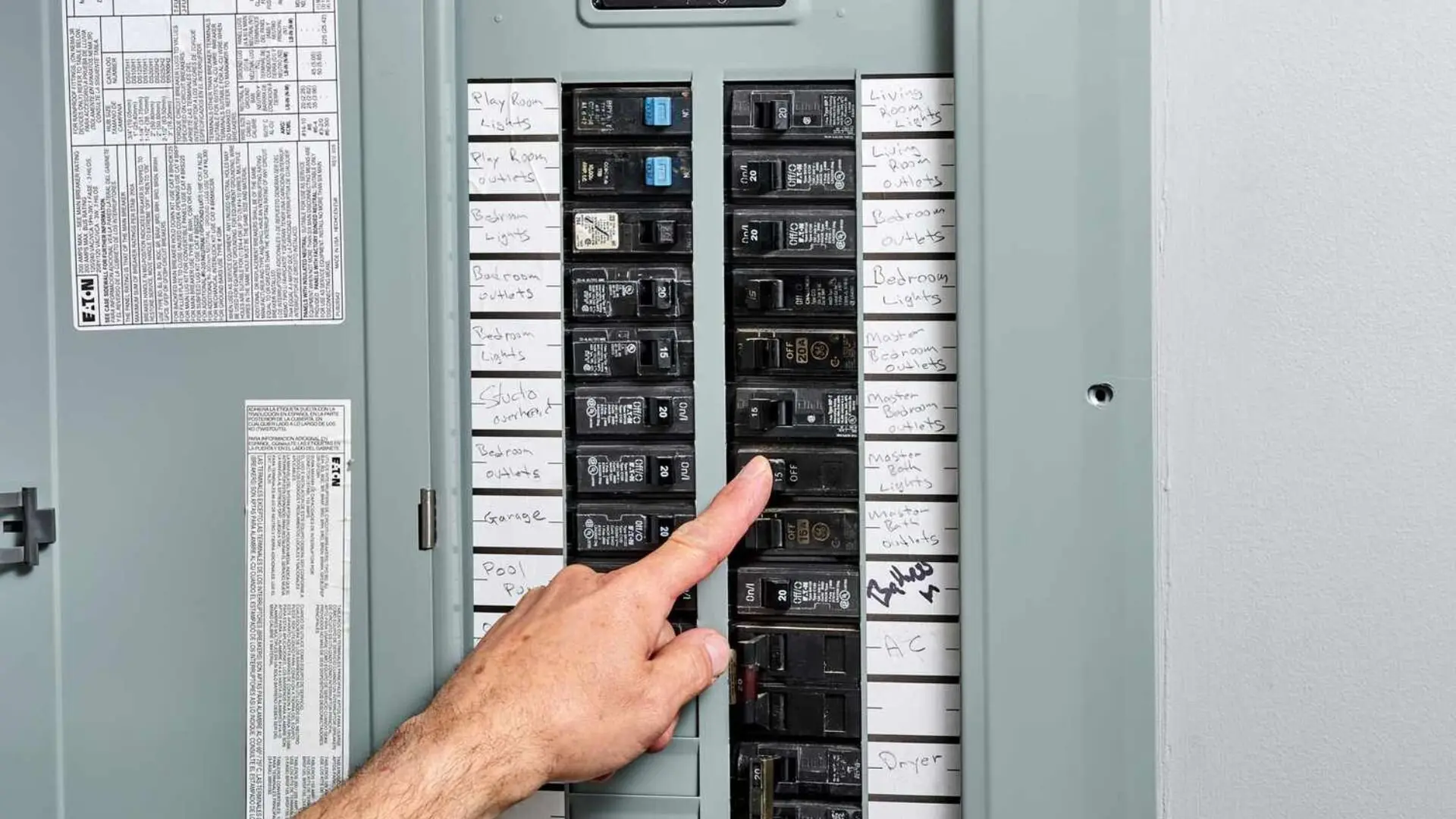
Types Of Circuit Breakers
Various circuit breakers are available to cater to different electrical system requirements. Let’s explore some common types of circuit breakers and their essential functions.
![2023 07 Different Labelled Circuit Breakers Labelled Circuit Breakers]()
Main Breaker
The main breaker is a crucial component within the electrical panel. It serves as a master switch that controls the entire electrical system. When the main breaker is turned off, it cuts off the flow of electricity to all the lights, outlets, and appliances connected to the electrical panel.
Single Pole Circuit Breakers
Single-pole circuit breakers are commonly used in residential settings. They are designed to handle 120-volt circuits and are typically used for lighting, outlets, and small appliances. These breakers connect to a single wire and protect against overloads and short circuits in specific circuits.
Double Pole Circuit Breakers
Double-pole circuit breakers are used for higher-voltage circuits, typically 240 volts. They consist of two wires commonly found in larger appliances like air conditioners, electric water heaters, and electric stoves. Double-pole breakers provide enhanced protection against overloads and short circuits in these high-voltage circuits.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs)
GFCIs are specialised circuit breakers designed to protect against ground faults. They monitor the flow of electricity and detect any imbalance between the hot and neutral wires. If a ground fault is detected, such as a current leakage due to damaged wiring or loose connections, the GFCI trips and interrupts the flow of electricity, preventing potential electrical shocks.
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs)
AFCIs are circuit breakers that protect against arc faults. They detect dangerous conditions caused by damaged or loose wire connections that can lead to fires. When an arc fault is detected, the AFCI trips and shuts off the power, preventing overheating and potential fire hazards.
Combination Type Circuit Breakers
Combination-type circuit breakers offer a combination of AFCI and GFCI protection within a single breaker. They provide enhanced safety by protecting against arc and ground faults, offering comprehensive electrical system protection.
It’s important to note that circuit breakers are designed for specific electrical panels and should be of the same brand as the panel to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. Always consult a qualified electrician for guidance when selecting and installing circuit breakers to ensure compliance with safety standards and prevent electrical hazards.
Is Your Electrical System Safe?
Circuit breakers are essential components of electrical systems, providing crucial protection and ensuring the safe operation of our homes and businesses. They play a vital role in safeguarding against hazards such as short circuits, electrical shocks, and potential fires.
Circuit breakers are important not only for their protective functions but also for their convenience. Unlike older systems like fuse boxes, circuit breakers can be easily reset after a trip, eliminating the need for constant replacement and providing a more efficient and reliable power supply.
Where electricity powers our everyday lives, circuit breakers are instrumental in maintaining a secure and efficient electrical infrastructure. It is crucial to consult qualified electricians to install and maintain your switchboard correctly and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Get in touch with Bright Force Electrical today to gain the peace of mind that only professional electricians can bring, safeguarding your home and electrical system for years.
FAQ’s
Can circuit breakers be reset after they trip?
Yes, circuit breaker tripping can be reset. When a circuit breaker trips due to an overload or a fault, it moves to a "tripped" position, disconnecting the circuit. To reset it, you must manually move the breaker handle back to the "on" position. However, it’s essential to identify and address the cause of the trip before resetting the breaker to prevent recurring issues or potential hazards.
Do circuit breakers require maintenance?
While circuit breakers are generally reliable, they require periodic maintenance to ensure proper functioning. Routine inspections can help identify any signs of wear, damage, or malfunctioning components. Cleaning the breaker contacts and tightening any loose connections are standard maintenance practices. Additionally, if a breaker frequently trips, it may indicate an underlying issue that needs to be addressed by a qualified electrician.
How do you choose between circuit breakers and fuses?
The decision to use a fuse or circuit breaker depends on factors like protection level, cost, convenience, response time, and maintenance. While both have the same basic function and work on the same principle as an electrical safety device, circuit breakers offer better protection, can be reset, and require less maintenance, but can be more expensive.
Fuses are cheaper and have a faster response time but need replacement when blown. Consider the specific requirements of your electrical system and consult with a professional to determine the most suitable choice.
Do I need high and low-voltage circuit breakers?
To choose between high and low-voltage circuit breakers, consider factors such as voltage level, system application, current rating, fault level, standards and regulations, and operational features. High-voltage circuit breakers suit systems above 1,000 volts, commonly found in utilities and industrial facilities. In comparison, low-voltage circuit breakers are suitable for systems below 1,000 volts and are often used in residential and commercial settings.
Ensure the circuit breaker matches your system’s voltage, current, and fault level requirements while complying with safety standards. Assess operational features like remote control or protection functionalities. Consulting electrical experts can provide further guidance for the optimal choice.