![2023 12 Man Fixing Switchboard (1) Man Fixing Switchboard ()]()
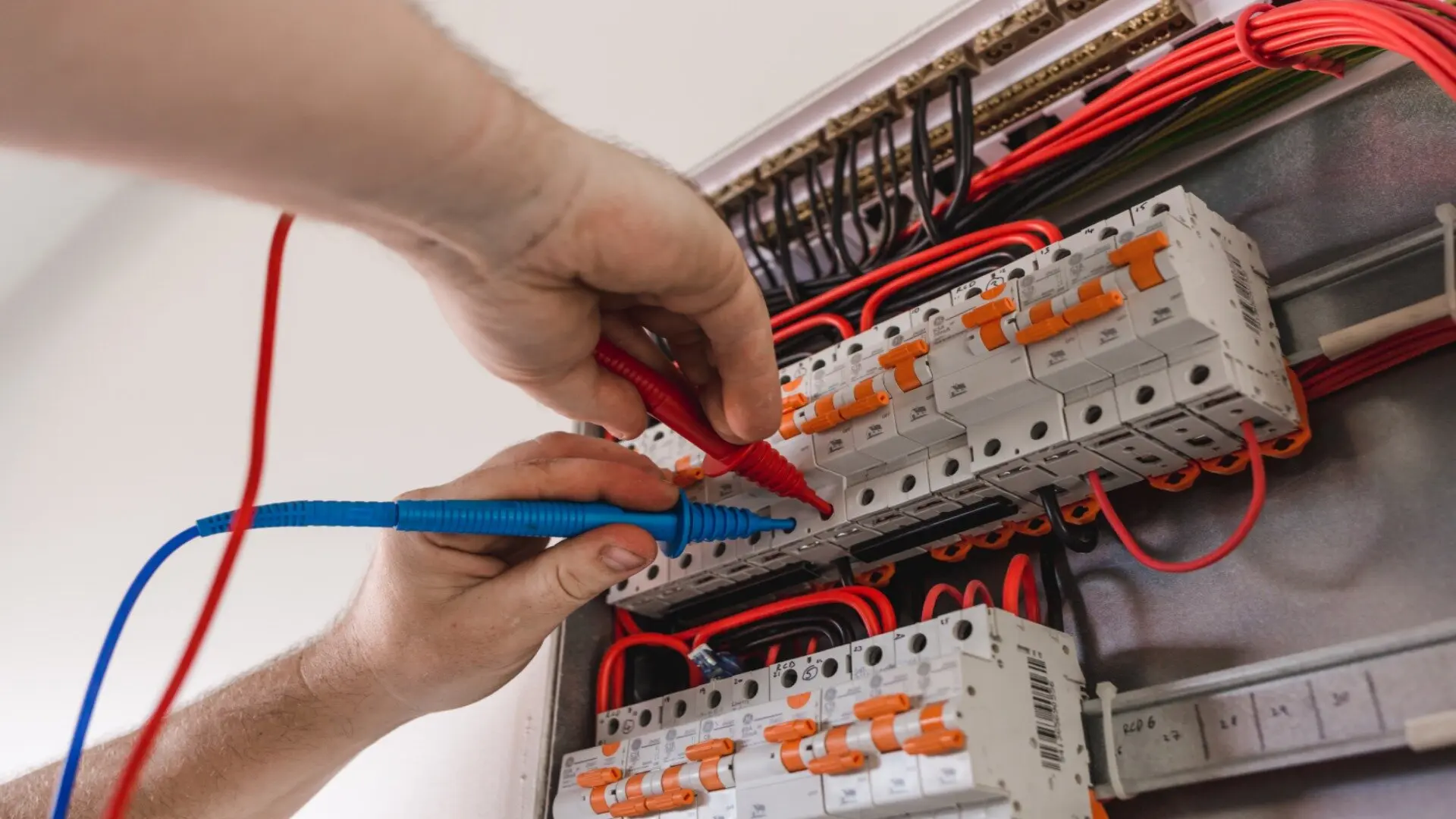
Switchboards are the behind-the-scenes heroes that keep electricity flowing safely within buildings and facilities. While we don’t give them much thought, these large electrical panels are vital in power distribution. But what exactly is a switchboard?
It’s a centralised hub that routes and regulates electricity from the main supply to individual circuits across a site. The switchboard houses critical components like circuit breakers, switches, bus bars, and more to direct and protect power distribution.
Grasping the basics of a switchboard’s components and how certified electricians install and maintain them is key to ensuring these systems run smoothly. This article will delve into the essence of switchboards, how they’re set up, their critical components, and why they’re vital for managing electricity in your facility. We’ll illuminate the details of how switchboards work!
What is a Switchboard Exactly?
A switchboard is the hub that directs and controls power distribution in a building or facility. Housed in a large metal enclosure, the switchboard is a centralised panel that receives electricity from the electrical utility or generators and then distributes it safely using protective devices like fuses and circuit breakers.
Large conductors called bus bars are the main power distribution rails inside the switchboard. They direct electricity to the various branch circuits supplying the facility. The switchboard also contains switches and meters to control and monitor electrical loads.
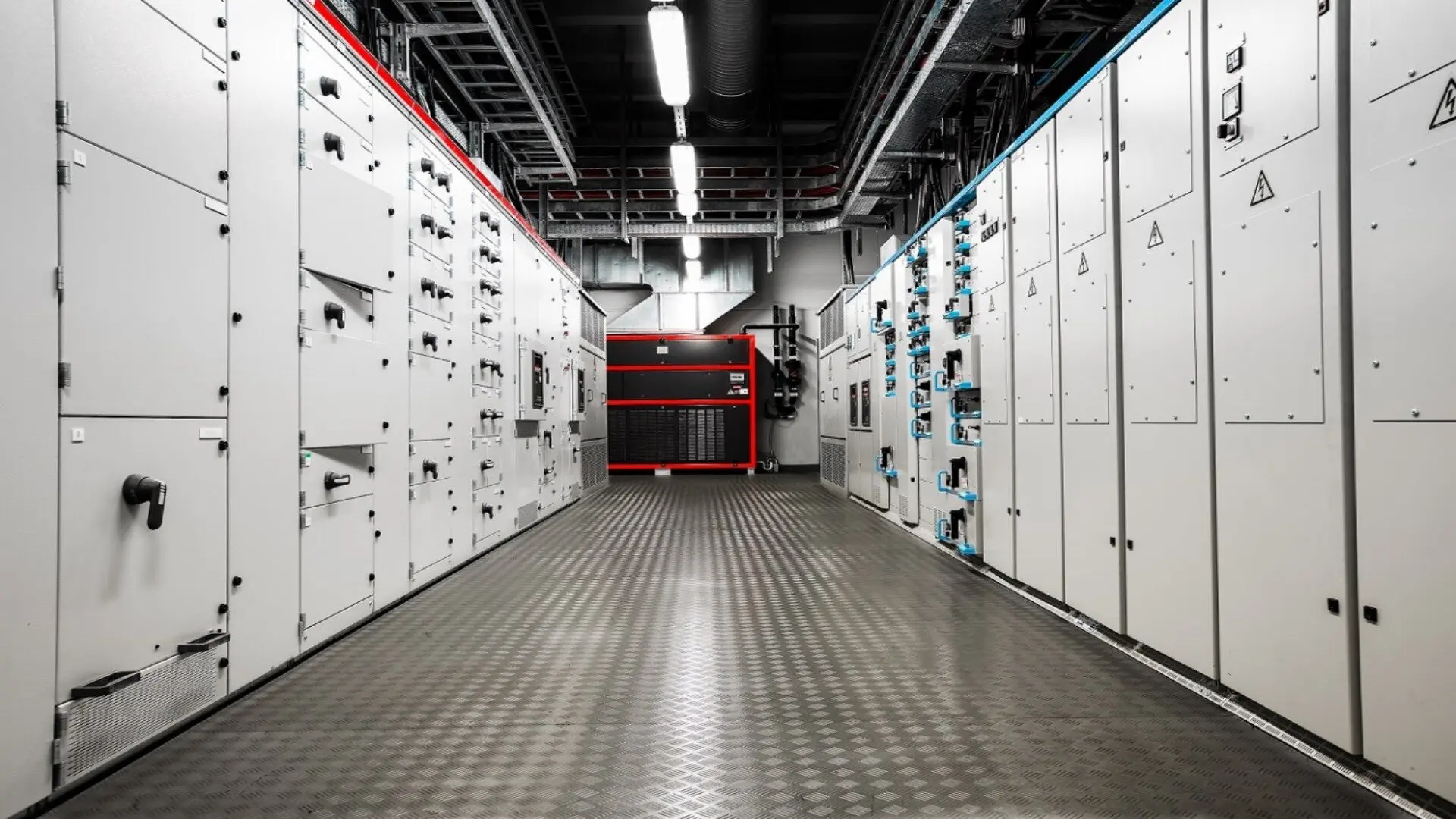
![2023 12 Switchboard Hallway Switchboard Hallway]()
Beyond the standard parts, switchboards might also feature voltage regulators, surge suppressors, and power factor correction capacitors. The main roles of a switchboard include distributing electricity, offering overcurrent protection, enabling the safe isolation of circuits, and providing tools to monitor and control power usage.
Switchboards vary according to building size. In smaller facilities, a service entrance switchboard may be installed. This means that power is directly fed from an electrical provider. Large buildings require a more complicated system.
A switchboard in commercial buildings may receive indirect power from an upstream circuit breaker. Proper installation and maintenance by qualified electricians keep these complex switchboards running smoothly.
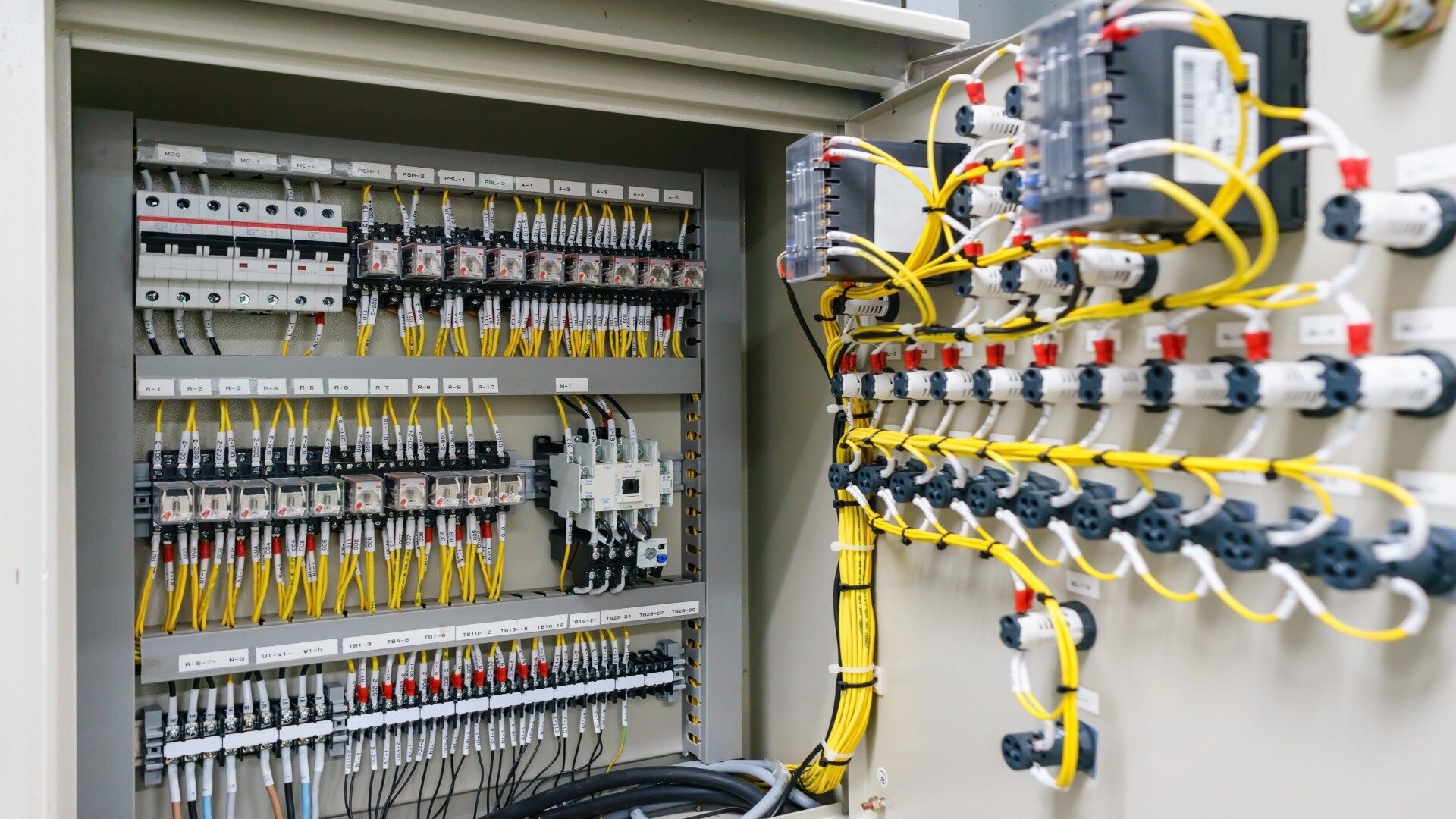
Critical Components of a Switchboard
Inside an electrical switchboard, you’ll typically find these main components:
Bus Bars
These thick strips of copper or aluminium act as the main power distribution rails. The incoming supply and branch circuit breakers receive electricity by connecting to the bus bars.
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers provide overcurrent protection and allow power to be disconnected from individual branch circuits for safety. They trip open automatically when electrical faults are detected.
Fuses
Fuses operate similarly to circuit breakers, opening the circuit when overloads or faults occur. They are older protection devices but are still found in some switchboards.
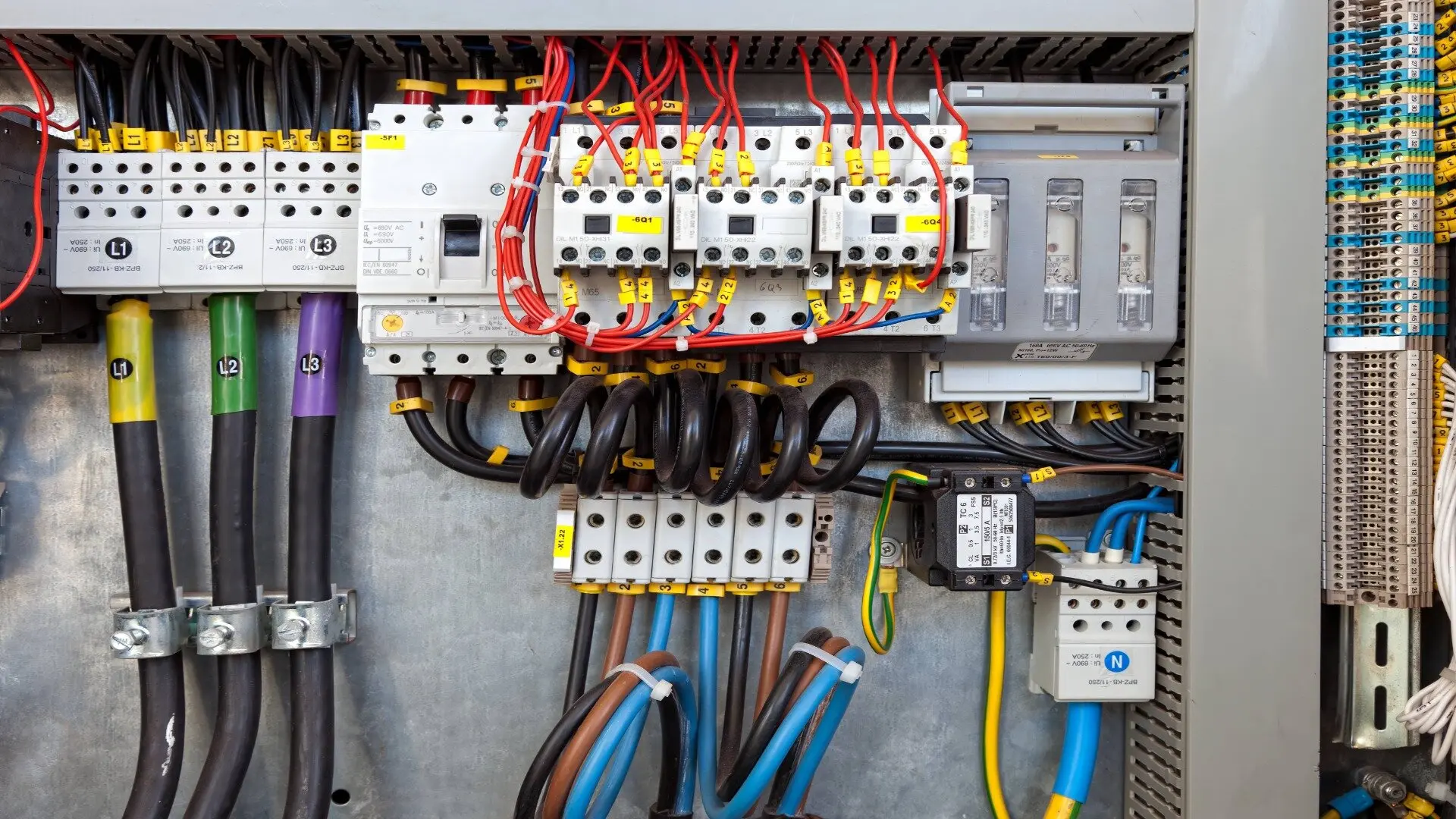
Switches
These manually operated switches allow operators to isolate electrical equipment for maintenance or de-energise circuits in an emergency. Switches vary based on amperage ratings.
![2023 12 Electrical Switchboard Electrical Switchboard]()
Meters
Digital or analog meters display vital data such as voltage, amperage, and power consumption to monitor the electrical system.
Ground Bus
The ground bus bar connects all component grounding wires as a central grounding point.
Power Connections
Locations where incoming utility or generator power enters and exits the switchboard.
Control Wiring
Contains low voltage control wiring for any automated systems.
Safety Features
Components like arc flash barriers and insulated gloves or mats protect workers from live current exposure.
An Integrated Facility System (IFS) is an excellent option for your switchboard because you can integrate other components with your system to expand your setup.
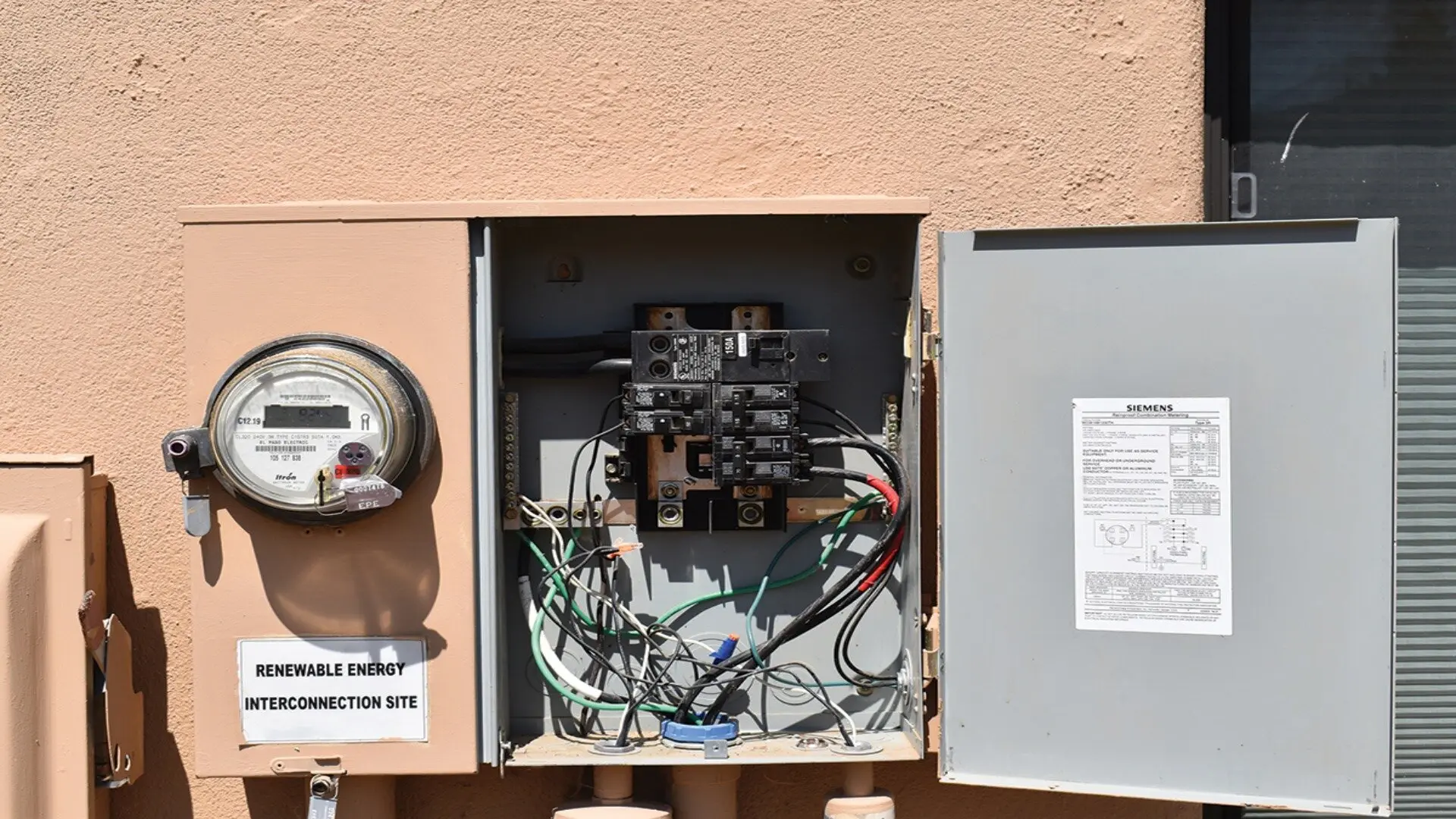
How Power Enters and Leaves a Switchboard
The electricity supply enters the switchboard through a main protective device, such as a main circuit breaker or set of fuses, typically rated for the full amperage capacity of the electrical service. These main electrical disconnects allow the entire switchboard to be safely isolated for maintenance when needed.
Once inside the switchboard, power travels across bus bars, ready for distribution to individual branch circuits that supply equipment throughout the facility. Each branch circuit has its own circuit breaker or fuses, specifically guarding that circuit.
![2023 12 Electrical Panel Safety Electrical Panel Safety]()
These branch circuit breakers or fuses tap power off the main bus bars and deliver it through outgoing cables to feed lighting panels, appliances, machinery, and receptacles across the building. When electrical loads turn off or trip their protective devices, the branch circuit becomes de-energised, but the main bus bars remain with power.
Additional switchboard components like meters, switches, and capacitors are wired to the live bus bars to perform their roles. Fusible panelboards and switchboards are used to protect and switch feeder and branch circuits – and each panelboard unit comes with a switching contact structure with an instant switch element for safety and accurate energy current direction.
These switchboards are explicitly designed for commercial and industrial sites – and are helpful for service entrance switchboards. Proper installation by a licensed electrician ensures safe entry and exit of electricity in the switchboard.
Circuit Breakers Protect the System
Circuit breakers are vital protective devices within a switchboard that constantly monitor the current flow and automatically trip open if electrical faults are detected. They are usually connected to the main incoming power supply, and each branch circuit distributes electricity throughout the facility.
The power breakers adjust trip settings based on the amperage ratings of the wires and equipment they protect. If the current flowing through a circuit breaker exceeds the safe limit due to an overload or short circuit, the mechanism inside the breaker will rapidly open or “trip” the electrical contacts.
![2023 12 Commercial Electrical Panel Commercial Electrical Panel]()
This cuts power to that circuit and prevents damage or fire. When manually tripped, circuit breakers also act as local on or off switches for their circuits. Newer “smart” computerised circuit breakers can communicate detailed diagnostic data.
Proper circuit breaker selection, coordination, and maintenance ensure optimum protection and selective tripping when faults occur in complex switchboards. The fast-acting circuit breakers provide a reliable means of isolating faulted circuits to keep the rest of the system up and running.
Measuring and Monitoring Electricity Flow
Electrical switchboards incorporate a range of tools to measure and monitor circuit distribution. For a more comprehensive setup, you might add datacom equipment, distribution transformers, or uninterruptible power supplies, centralising all your facilities. Digital ammeters show current flow in amps for both incoming and outgoing circuits, making it easier to spot overloads.
Voltmeters show if the voltage is within normal range or fluctuating. Power meters calculate kilowatt usage to track energy consumption. Indicator lights convey status conditions.
![2023 12 Electrical Control Electrical Control]()
Alarm systems alert operators to potential issues. Data loggers record electrical parameters like power factor for analysis. Advanced switchboards have communication capabilities to integrate metering with building management systems for remote monitoring.
Accurate real-time data on electricity flow enables informed system control, rapid fault detection, and predictive maintenance. Qualified technicians routinely verify that switchboard meters stay properly calibrated.
Quality meters, monitoring, and trend data keep facility managers fully informed of power usage and electrical system performance, improving efficiency, safety, and reliability.
How Switchboards Are Installed and Maintained
Installing and maintaining switchboards calls for specialised technical knowledge. Proper sizing and planning to match the facility’s power needs and distribution scheme are also crucial.
Qualified electricians handle the physical installation following all electrical codes and standards. Proper feeder wiring, grounding, and connections are made to integrate the switchboard safely.
![2023 12 Understanding Electrical Panels Understanding Electrical Panels]()
The equipment is tested and configured before being powered up and operated. Once running, certified technicians perform routine inspections, testing, and preventative maintenance to keep the switchboard in peak operating condition.
This involves using IR scanners to check for hot spots, verify tight connections, clean, lubricate, inspect components for wear, and exercise moving parts. Any issues get repaired immediately. Upgrades or replacements are done as needed over time.
Proper maintenance prevents problems, minimises downtime, and extends the reliable service life of the switchboard. Only trained personnel should access internal switchboard components due to hazardous live voltages. Following safety procedures is critical.
Work Safely with Switchboards
Now that we’ve explored switchboards and how they operate, you can appreciate their vital role in electrical systems. Though often hidden from view, switchboards are the backbone of power distribution in facilities.
Understanding what’s packed inside these panels and their role in safely managing electricity gives you a deeper appreciation for an electrician’s crucial work. Though switchboards might appear complex initially, their careful setup, upkeep, and monitoring by skilled technicians ensure the lights stay on without a hitch.
Bright Force Electrical has the experience and expertise to handle all your switchboard needs. If you have an upcoming switchboard project or need a qualified assessment of your current system, please call us.
Our master electricians can keep your switchboard running optimally for years to come. Investing in professional switchboard services ensures reliable power delivery for your facility.




.jpg)